Sorry Mr. President, But The Affordability Crisis Isn't A 'Hoax'
It was yet another performance that left us wondering about President Donald Trump’s failing mental faculties. Speaking to supporters at a rally in Mount Pocono, Pennsylvania last week, Trump was typically unhinged.
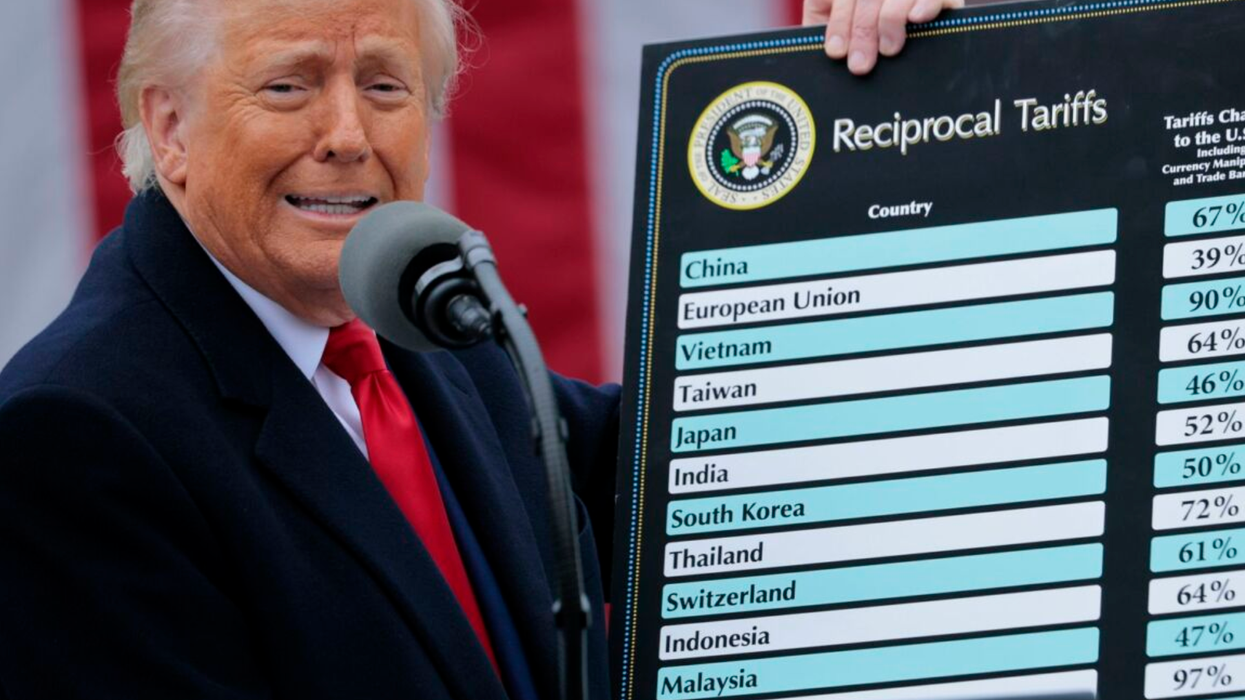
And we have two price charts. Do you remember the last time I pointed to a chart? I don't care what these charts say. My all-time favorite chart was the chart I had in Butler. I said, "Let's look at the chart." I don't care how good that chart looks, it's shit by comparison to the one in… It's nothing. I like the Butler chart. Remember that was on how great employment was and all this, but I like it for other reasons. Look at that chart. It's good. But now that I talk about the Butler chart, I don't even want to look at it, doesn't mean anything. But look, Biden price increases and Trump price increases. Look at Biden. Up 37, 24%, 22, 21, 30.7, 30.7 again, 10.4%, 49%. Trump, the price is down 5.1, 4.2, 0.5, down 4%, 2.9. Look at that. Our prices are coming down. Their prices, it's a hoax. They're just … Remember they said the Inflation Reduction Act, remember that? Billions and billions, hundreds of billions of dollars, the inflation, and after they got it approved, because we had a few Republicans that went along with that whole hoax.
If there was a coherent thought buried in all that gibberish, he later tried to summarize it this way: “Prices are coming down very substantially. But they have a new word. They always have a hoax. The new word is affordability.”
He can call it a hoax all he wants, but Trump and his team know affordability is a real problem. That’s why he’s suddenly trying to co-opt the term, like a cringe Truth Social post declaring himself “THE AFFORDABILITY PRESIDENT.” It’s also why his team has sent him out on what it’s calling an “affordability tour,” which is how he ended up in Mount Pocono at the Mount Airy Casino Resort. The largest ballroom there holds about 1,200 people—a telling choice by a campaign clearly afraid of empty seats at a sizable venue.
What should worry Republicans is not just the optics, but the substance. A rally supposedly designed to counter Democratic attacks on affordability instead showcased Trump creating an entire alternate reality.
“We’re getting inflation,” he said. “We’re crushing it, and you’re getting much higher wages. I mean, the only thing that’s really going up big, it’s called the stock market and your 401(k)s that’s going up.”
That line should sound familiar, because Democrats already tried it—and paid the price. President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris spent much of the 2024 campaign insisting the economy was strong, that inflation was cooling, that wages were up, and that voters simply didn’t understand how good things really were.
Voters didn’t buy it. Telling people they’re wrong about their own financial stress is a losing message, no matter which party delivers it.
Trump is now making the exact same mistake, only he’s louder and more detached from the lives of the people he claims to be fighting for. Instead of acknowledging the pain people are actually feeling, he reached for a familiar crutch: bragging about the stock market, as if that is supposed to mean something to an audience in Appalachia or to anyone struggling to pay rent or buy groceries.
And he couldn’t stop.
“The stock market has set 51, this is in less than 10 months,” Trump said. “The stock market has set 51 all-time record highs. There’s never been anything like that. Bum, bum, bum, bum, bum, bum.” He repeated the claim again for good measure.
Then came a reprise of the “let them eat cake” routine he’s been workshopping for a while. After bizarrely claiming that without his tariffs “you would have no steel,” Trump explained that Americans should simply do without other consumer goods.
“You can give up certain products. You can give up pencils because under the China policy, every child can get 37 pencils. They only need one or two,” he said. “You don’t need 37 dolls for your daughter. Two or three is nice, but you don’t need 37 dolls.”
It’s remarkable watching so many cultish conservatives swing from “Don’t tread on me” to “Please daddy Trump, tell me how many dolls my daughter can have.” For the broader electorate, though, this message is political poison.